Jamabandi Haryana Land Records
Jamabandi is a document which includes the Record of Rights as well as records of cultivation, ownership, and the most recent information of several rights in land.
Every 5 years, the Jamabandi is revised which is put together by Patwari and the respective Revenue Officer attests the document. While one copy is entrusted with the District Record Room, the second copy is retained by the Patwari.
The Jamabandi portal or website is the initiative of the Revenue Department of Haryana developed by utilising technology to update and record land details. The portal is developed to enable citizens to obtain land records of the state of Haryana. You can access land records such as mutation, registration and Jamabandi (Records of Rights).
Features and Benefits of Jamabandi
Below are the features and benefits of the Jamabandi portal:
- Checklist for Deed Registration.
- Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Deed Registration.
- Deed templates.
- Collector rates.
- Check Deed appointment availability.
- View registered Deeds and stay orders.
- Controlled/urban area details.
- Nakal details by owner name.
- View mutation orders.
- Check the status of the mutation.
- Mutation status of Deeds.
- View cadastral maps.
- Check revenue court status or civil court status.
- Check property tax details.
- Integrated property wise transaction details.
Also, you can find details about:
- Owner of the property
- Kashatkar
- Makbuja
- Total land
- Irrigation
- Majrua
- Gair majrua
- Khewat/khatoni
How to Check Availability of Deed Registration Appointment Slots in Jamabandi
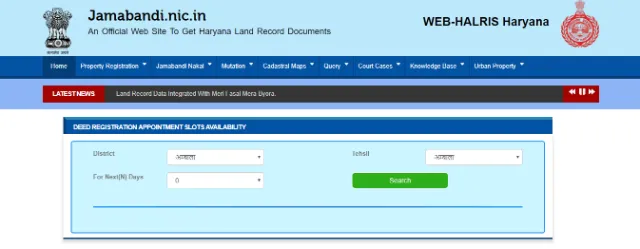
Below are the steps to check the availability of the Deed registration appointment slots through the Jamabandi portal:
- Visit for Jamabandi Appointment Slots
- Select the district, tehsil and choose the number of days you would like to know the availability of slots.
- Upon searching, you'll be able to view the availability of the slots.
How to View Jamabandi Land Nakal Online
To view the Nakal record through the Jamabandi website, follow the below steps:
- Visit Jamabandi Nakal Record.
- Here you can choose to search by owner name/khewat/khasra/date of mutation.
- Select the district, tehsil/sub-tehsil, village, and the Jamabandi year.
- Select the owner and you'll be able to view the Nakal details.
How to Search Registered Deeds Online in Haryana
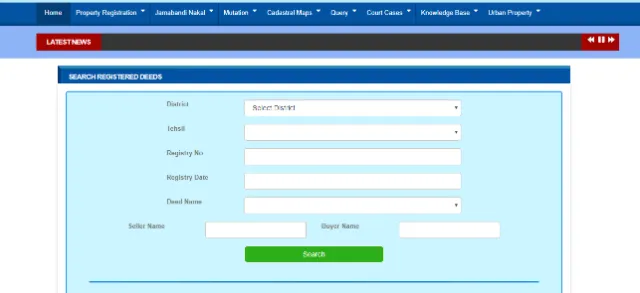
The Jamabandi portal lets you search for registered deeds online. Below are the steps:
- Visit Jamabandi Land Registered Deeds.
- Select the district, tehsil, registry number, registry date, deed name, the seller name, and the buyer name.
- Click on 'search' and you'll be able to find registered deeds.
How to Search Court Cases and Download Order Online
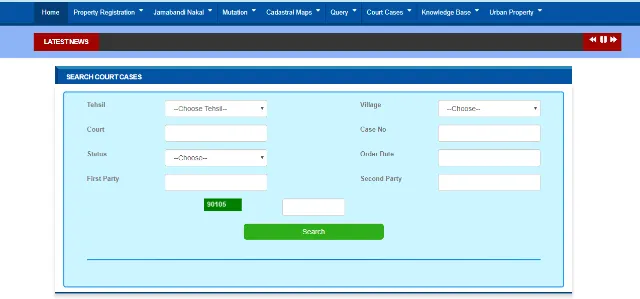
If you want to find out court cases, if any, on a property and download the order online, you should:
- Visit Jamabandi Court Case Order Online.
- Select the tehsil, village, court, case number, status (stay/attachment/disposed), order date, first and the second party, and enter the captcha code.
- Upon clicking on 'Search' you'll be able to find the court case and download the order.
How to View Mutation Orders in Jamabandi
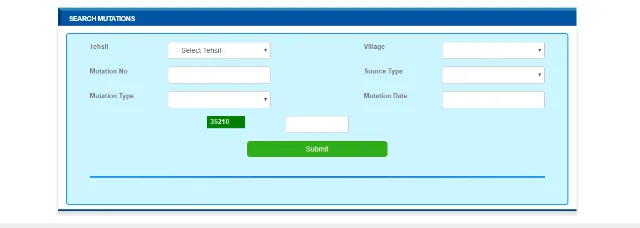
To view mutation orders through the Jamabandi website, follow the below steps:
- Visit Jamabandi Mutation Orders.
- Select details such as tehsil, village, mutation number, source type, mutation type, and the mutation date.
- Click on 'Submit' to view the mutation order.
How to Check Mutation Status Online
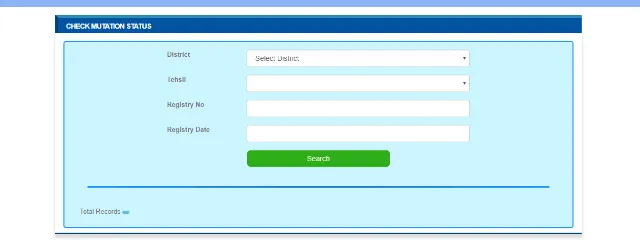
To know the status of a mutation online, follow the below steps:
- Visit Jamabandi Mutation Status.
- Select the district, tehsil, registry number, and date.
- Upon clicking on 'Search', you'll be able to check the mutation status.
What is mutation?
Mutation relates to the changes required to be made regarding the title and ownership of land.
- Sale
- Gift
- Exchange
- Mortgage with possession
- Mortgage without possession
- Mutation of changes in ownership due to decrees in civil court
- Mutation of inheritance
- Partition
- Land term leases
- Redemption of mortgage
Mutation Fee
Rs.250: For entries related to the acquisition of an interest or right by a registered deed or an order of court or a decree or order of a Revenue Officer affirming or making a partition under Chapter IX of the Punjab Land Revenue Act, 1887, or if directing the incorporation in the record of acquisition of an interest or right by inheritance, or a private partition.
Rs.50: This will be service charges per mutation which has to be deposited at the district level at the District Information Technology Society (DITS).
How to View Cadastral Map in Jamabandi

To view the cadastral map:
- Visit jamabandi Cadastral Map Online.
- Under the drop-down menu, select 'Cadastral Maps' and choose 'View Cadastral Maps'.
- You'll be re-directed to https://hsac.org.in/eodb/.
- Here you can search by district, tehsil or village, or all.
How to Check a Revenue Court Case Status in Jamabandi
Jamabandi offers the service to check revenue court cases' status online. Below are the steps:
- Visit Jamabandi Official Site.
- Under the drop-down menus, select 'Court Cases'.
- Select 'Revenue Court Status' and you'll be re-directed to Haryana Revenue Courts Site.
- On the left-hand side of the page, select 'View Case Status'.
- Enter the required details such as location, court, petitioner advocate or petitioner name, case ID or case number and click on submit to view the status.
How to Check Civil Court Case Status in Jamabandi
To check a civil court case status online, follow the below steps:
- Visit Jamabandi Land Record Case Status.
- Enter the required information such as district, tehsil, village, mustil, and khasra number.
How to Register an Immovable Property in Jamabandi
Below are the steps to register an immovable property:
Step 1 - All information pertaining to the property value as per the rate of the Collector, charges such as stamp duty, service charges, registration fee as well as the instrument formats can be procured from the respective Joint Sub-Registrar/Sub-Registrar's office HARIS counter.
Step 2 - Based on the property value at the rate of the Collector, stamp papers with value of up to Rs.10,000 can be procured from stamp vendors and for stamp duty of more than Rs.10,000, stamp papers can be procured from the treasury office after the required amount is deposited in the SBI with "0030-Stamp and Registration" as the under head.
Step3 - Upon obtaining the required stamp papers, you can write the document, or it can be written by a document writer, and two witnesses are required during the execution of the process. Along with the stamp papers, you'll have to submit a copy of the title deed, copy of the map, Jamabandi, digital photograph, plan, etc.
Step 4 - The set of documents along with the stamp papers needs to be submitted to the respective Sub-Registrar office where the property is located.
Step 5 - The submitted documents will be examined carefully by the Sub-Registrar and the amount paid towards stamp duty, service charges, and the registration fee through the HARIS system.
Step 6 - After the scrutiny of documents, you'll have to appear before the Joint Sub-Registrar/Sub-Registrar for the entry of the said document. To authenticate the executant's identity, two witnesses are required to be present.
Step 7 - Upon endorsing the entry of the executant by the Joint Sub-Registrar/Sub-Registrar, subject to adherence to procedures, the respective Sub-Registrar will include the registration certificate, through the computerised HARIS system, on to the documents.
How to check collector rates on the Jamabandi Portal
To check collector rates on the Jamabandi portal, you need to follow the steps mentioned below:
- Visit Jamabandi Official Website
- Click on 'Collector rates' under the 'Property Registration' tab
- Select correct 'District', 'Tehsil', 'Period' and 'Village' from the drop-down menu
- Click on 'Submit'
- You will be displayed the rates as per segment, property and property sub-type
Find Land Records in Other States
Schemes and Acts
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana - Urban - PMAY(U)
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Gramin Online (PMAYG)
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana - Urban 2026
- Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016
- Stamp Duty and Registration Charges 2026
- Encumbrance Certificate (EC)
- Delhi Development Authority (DDA) Housing Scheme
- Land Records 2026
FAQs on Jamabandi Haryana Land Record
1.Who must pay the stamp duty in the case of a conveyance deed, sale deed, lease/rent deed, exchange deed, and partition deed?
In the case of conveyance/sale deed, the purchaser must bear the stamp duty, while in the case of lease/rent deed, the lessee is liable to pay the stamp duty. As for exchange deeds, both the lessee and the lessor must bear the charges equally. In the case of a partition deed, stamp duty is payable as per the respective shares of the lessee and the lessor. In other cases, the charges are usually paid by the executant.
2.Are you bound to pay registration fees and stamp duty on the value of the rate of the Collector?
Under Section 47-A of the Indian Stamp Act, 1899, you're not required to pay the said charges on the value of the rate of the Collector under consideration and the exact stamp duty amount and the registration fee is payable.
3.What is the time frame to get the documents registered?
All documents except Will need to be registered within four months from the date it was executed under Section 23 of the Registration Act, 1908. However, under Section 25 of the Registration Act, 1908, upon the payment of the prescribed fine not more than 10 times of the registration fee, you can delay the registration of documents for up to 4 months.
4.What is the charge of stamp duty for different instruments?
Conveyance/Sale Deed: 8% in urban areas and 6% in the rural areas. Exchange Deed: 6% of the greatest value in rural areas, while it's 8% of the greatest value in urban areas. Gift Deed: 3% and 5% in rural and urban areas, respectively. SPA/GPA: Rs.100/Rs.300. Partnership: Rs.22.50. In case of a Sale Deed in favour of a woman: 4% and 6% in rural and urban areas, respectively.

Disclaimer
Credit Card:
Credit Score:
Personal Loan:
Home Loan:
Fixed Deposit:
Copyright © 2026 BankBazaar.com.
